Botswana's Diamond-Funded Healthcare System: A Journey from Failure to Reform and Rebuilding
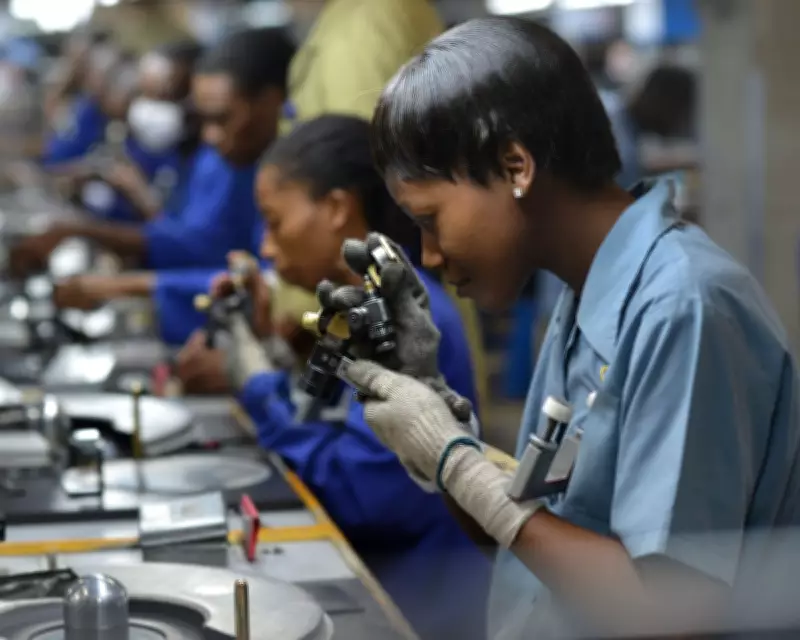
Botswana, a nation renowned for its diamond wealth, has long relied on these precious resources to fund its public healthcare system. However, this diamond-funded model has faced substantial challenges, leading to widespread failures in service delivery and patient care. In recent years, the country has embarked on a comprehensive reform and rebuilding initiative to address these shortcomings and enhance the overall health infrastructure.
Historical Context and Initial Failures
The healthcare system in Botswana was initially established with significant investments from diamond revenues, aiming to provide universal access to medical services. Despite these financial injections, the system struggled with inefficiencies, including inadequate facilities, shortages of medical personnel, and poor management practices. These issues resulted in long waiting times, limited access to specialized care, and substandard treatment outcomes for many citizens.
Reports indicated that rural areas were particularly affected, with clinics often lacking essential equipment and medications. The reliance on diamond funding also created vulnerabilities, as fluctuations in the global diamond market impacted budget allocations for healthcare. This led to a cycle of underfunding and neglect, exacerbating the system's failures and undermining public trust.
Reform Initiatives and Rebuilding Efforts
In response to these challenges, Botswana has implemented a series of reforms aimed at overhauling the healthcare system. Key measures include increasing government oversight, investing in infrastructure upgrades, and enhancing training programs for healthcare workers. The rebuilding efforts focus on constructing new hospitals and clinics, particularly in underserved regions, to ensure equitable access to care.
Additionally, the government has diversified funding sources beyond diamonds, incorporating partnerships with international organizations and private sector investments. This strategic shift aims to create a more sustainable financial model, reducing dependency on volatile diamond revenues. Emphasis has also been placed on improving administrative efficiency and adopting modern medical technologies to boost service quality.
Current Status and Future Outlook
Today, Botswana's healthcare system shows signs of improvement, with enhanced patient outcomes and greater accessibility reported in many areas. The reforms have led to better staffing levels, reduced waiting times, and increased availability of essential medicines. However, challenges remain, including the need for ongoing investment and addressing persistent disparities between urban and rural healthcare services.
Looking ahead, Botswana continues to prioritize healthcare as a critical component of national development. Future plans include expanding telemedicine services, strengthening preventive care programs, and fostering innovation in medical research. By learning from past failures and building on recent reforms, the country aims to establish a robust and resilient healthcare system that can effectively serve all its citizens.